We talk about taxes and fees a lot in estate planning because if you don’t have a quality plan in place your estate will likely be hit with taxes and fees to a varying degree. Actual figures depend on the gross value of your estate, what state you lived in, and what strategies you employed (such as a living revocable trust) that help to reduce or even eliminate taxes and fees.
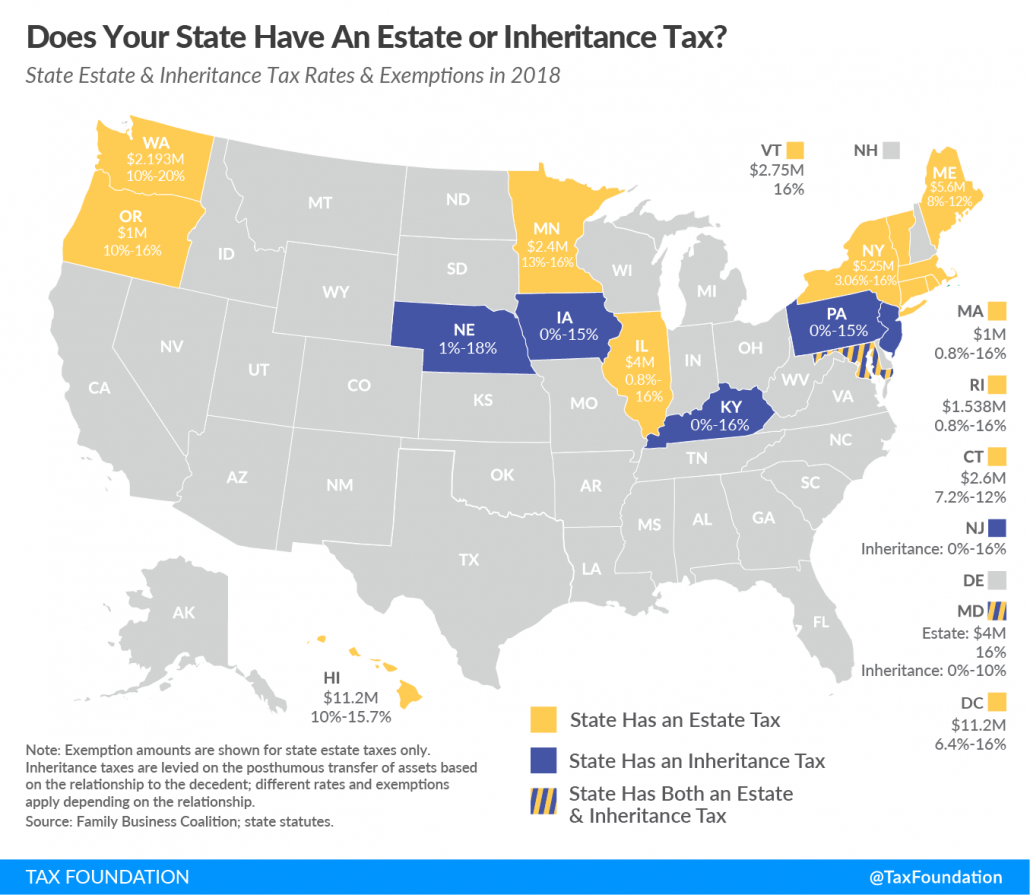
Recently I wrote about one specific tax that only applies to states—the state estate tax. If you don’t have time to read the full post and live in Iowa, the bottom line is that generally you won’t need to worry about it. Unlike places like Minnesota and Illinois, Iowa does not have a state estate tax. However, Iowa DOES have a special “death tax” that only six states in the U.S. have.
What is an Inheritance Tax and how is Different than an Estate Tax?
At first glance the inheritance tax seems mighty similar to the estate tax (both state and federal). Indeed, both are collected after someone’s death. However, an estate tax is assessed by the overall gross value of a person’s estate. This figure totals up all assets passed to all beneficiaries, regardless of their relationship to to the decedent (the person who passed away).
Any estate taxes owed are paid out of the estate assets before beneficiaries receive their distributions. And, the estate executor is responsible for making certain any state or federal estate taxes owed are fulfilled.
The inheritance tax, instead, is a tax levied on assets and property certain beneficiaries have inherited from someone who has died. I say “certain” because in most states the relationship of the beneficiary to the person who died determines if inheritance tax is owed or not. Amount of tax owed is calculated on each eligible beneficiary’s share of the estate and the beneficiary’s relationship to the decedent.
The beneficiary subject to estate taxes is personally responsible for filing the tax. In Iowa this means filling out Form 706 and filing before the due date on the last day of ninth month after death.
Iowa’s Inheritance Tax
The good news in light of all this tax talk is that Iowa’s inheritance tax only applies in certain situations. Not every Iowan who passes away will render their heirs subject to more taxes. For instance, Iowa’s inheritance tax does not apply if the estate is valued at $25,000 or less.
The following, among others, are exempt from Iowa’s inheritance tax:
- Spouses
- Beneficiaries who are descendants including children (biological and legally adopted), stepchildren, grandchildren, and great-grand-children.
- Beneficiaries who are lineal ascendants such as parents, grandparents, and great-grandparents.
- Life insurance
- Annuities purchased under a retirement or employee pension plan
- Assets left to U.S. charitable, religious, and educational organizations
As you can see, most people won’t ever have to deal with Iowa’s inheritance tax. So, who isn’t exempt as a beneficiary? Domestic partners, friends, and non-lineal relatives such as nieces, nephews, siblings, aunts, uncles, and cousins are all subject to the inheritance tax on the assets they inherit. Assets bequest to corporations or social/fraternal organizations don’t fit the qualifications as “educational, religious, or charitable” and are therefore not exempt.
Iowa’s max inheritance tax rate is 15%. (Which is better than our neighboring state of Nebraska, which has the highest top inheritance tax rate of 18%.)
In case you were wondering, there is no federal inheritance tax to worry about.
How do I Know if my Estate or Beneficiaries will owe Taxes?

Consult with an experienced estate planner and other professional advisors so that may they thoroughly evaluate if your estate will be subject to estate or inheritance taxes. Regardless, it’s a good idea to start looking into strategies and estate planning tools to reduce the burden of (all) taxes on your beneficiaries.
One way to do that during your lifetime is to gift (cash or non-cash) assets during your lifetime. The gift tax rate is currently at $15,000. Meaning the IRS will allow you to give away up to that amount, per donee (person receiving the gift), every year, without facing a gift tax.
I also highly recommend consulting an estate planner and other related trusted professional advisors to review your estate planning goals, financial situation, and assets. There are all sorts of unique considerations people face in that demand a thorough review and thoughtful solutions.
Have any questions or owe inheritance taxes yourself? Don’t hesitate to contact me at gordon@gordonfischerlawfirm.com or by phone at 515-371-6077.